Rules for Visualization – Part 1: Ten Beliefs You Should Toss Out the Window
Meaning, discernment, and the fascinating relationship between words and images – this is what visualization is all about. If you not only know the rules for visualization, but also know which conventional wisdom and beliefs you should toss out the window, it makes it easier to translate concepts into visual language.
An excerpt from our bestseller “UZMO – Thinking with the Pen” by Martin Haussmann
SHARE ARTICLE
Belief #1: The simpler, the better.
Not necessarily. You could, of course, attempt to draw the world using only three lines – as long as it truly helped the observer to better understand your point. Usually, though, one of the greatest challenges for visualizers is to strike a balance between including the necessary amount of information and the desire to keep things simple. Albert Einstein is reported to have said: “Everything should be made as simple as possible – but no simpler.” Depending on the context and the topic, three lines may actually be all you need – sometimes, though, more is required.
Belief #2: The more creative, the better.
It depends. If you need to explain something complex, it’s often best to use the simplest and most common pictograms. A heart stands for love; thunderclouds represent conflict. These symbols may not be particularly original, but their meaning is immediately clear. Of course, if you’re trying to build in an element of surprise in a presentation, more unconventional visual translations will be more effective.
Belief #3: Every piece of content must be visually illustrated.
No. Pictograms are intended to clarify information and provide orientation – just like street signs. The more signs that line the street, however, the less able are you, as the driver, to read what is on each of them. Pictograms are also visual anchors, and they can only provide orientation if they are precisely positioned.
Belief #4: Every pictogram has a specific meaning.
No. Pictograms only have the meaning that you assign to them – and that meaning is frequently understood only in context. A light bulb may symbolize a new idea or it may represent the energy consumption of a household – it depends upon how it is being used. Because of this, every pictogram needs a spoken or written word that clarifies its meaning.
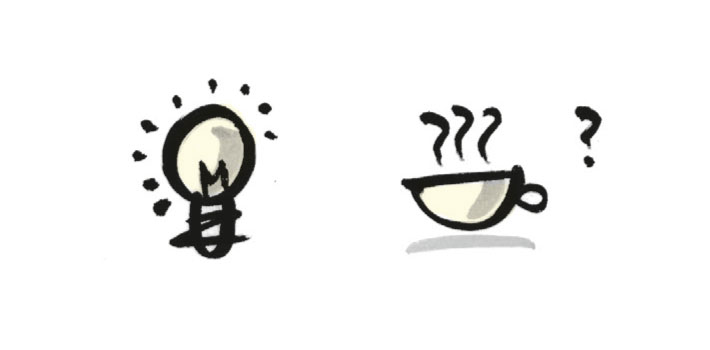
Belief #5: Visualization is a universal language.
Be careful! Every culture has its own visual code. Even within your own cultural circle, you cannot necessarily assume that everyone will interpret from your drawings the meaning you intend. For instance, not long ago, an Asian training participant had a question about our pictogram of a coffee cup (see above): “Why are those three noodles floating above the cup?” Globalization is, of course, helping visual language to become more consolidated. It’s still usually advisable to incorporate text to help ensure that meanings are made clear.
You can learn more about the most important visualization rules in Chapter 1 of the bikablo handbook: UZMO – Thinking With Your Pen. There, you can also learn how to transform information into images, how meaning is created, and which visualization techniques can be the most helpful to you.
MORE ARTICLES ON THIS TOPIC
You Might Also Be Interested In...
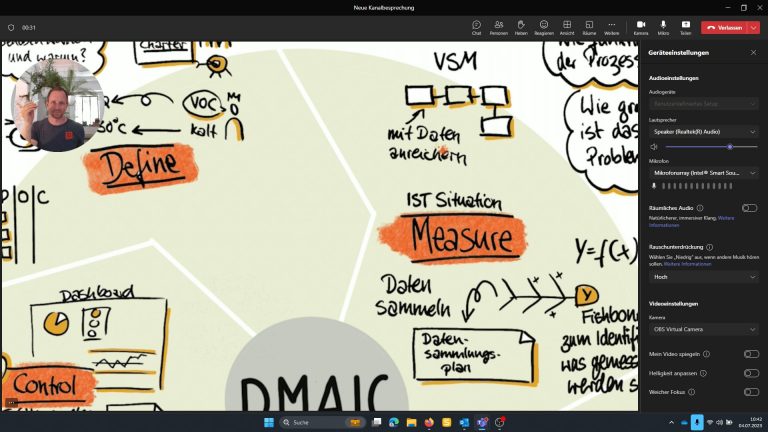
How to use your iPad instead of the webcam in MS Teams
Why do I want to connect the iPad to MS Teams (or Zoom)?
I would like to be able to show my iPad Screen as a tile in the normal Teams window. It should be subtle and not by sharing my screen to draw to much attention and to have a seamless switch between different views. I can i.e.
• document the meeting using OneNote or ProCreate
• easily zoom into pictures or drawing
• easily annotate pictures or digital whiteboards
• using the drawing feature while presenting your content
Design Thinking and Visual Thinking – a perfect fit?
In a recent interview Hiromi Hara speaks about her experience with applying the design thinking method with the help of visualization.
Hara explains that design thinking is not primarily about problem solving, rather about unveiling complex problems and getting better insight in the root cause of issues, hence the importance of the expression of individual perception and the comprehensible yet memorable depiction of thinking processes.
Using Visuals in Coaching
How our global trainer Jill Greenbaum got into drawing and which impact visualization has got on coaching situations.

